Don’t take chances with your health – secure the best care possible from one of the first surgeons to successfully treat complex benign gynecological conditions with minimally invasive surgery. With offices in Manhattan and Long Island, accessing the best ovarian remnant syndrome specialist in New York has never been easier.
What is ovarian remnant syndrome?
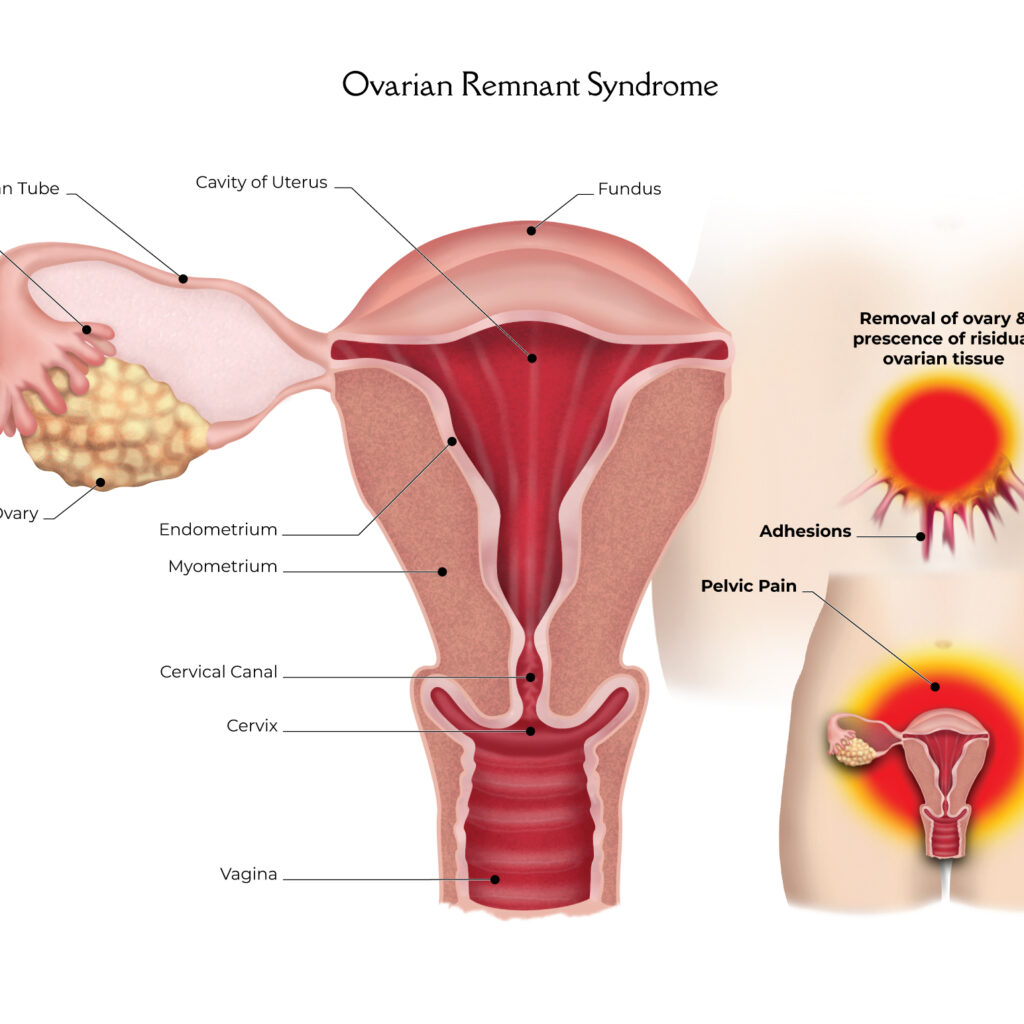
Ovarian remnant syndrome (ORS) occurs when ovarian tissue is unintentionally left behind following surgical removal of one or both ovaries (oophorectomy). It is a rare condition that is best treated by minimally invasive surgery.
It may be caused by circumstances during oophorectomy, which limit visibility or access to the ovaries, such as adhesions, endometriosis, inflammation, anatomic variations, or intraoperative bleeding.
Ovarian remnant syndrome is problematic because the ovarian tissue that is left behind responds to hormonal stimulation and can grow, bleed, become cystic, and reimplant on other organs such as the bowel or bladder and impede their function. It can result in a pelvic mass and rarely ovarian cancer.
What are the symptoms of ovarian remnant syndrome?
- Pelvic pain
- Painful urination
- Bladder dysfunction
- Painful bowel movements
- Bowel Dysfunction
- Painful intercourse
What treatment options does Dr. Nezhat offer for ovarian remnant syndrome?
Dr. Nezhat specializes in the application of minimally invasive surgical techniques to treat ovarian remnant syndrome. Laparoscopy and robotics are particularly well suited to treating ORS due to increased magnification and reach of the surgical instruments.
Dr. Nezhat has published extensively on the utility, safety and efficacy of minimally invasive surgery for gynecological pathologies.
Patients are often referred to Dr. Nezhat for treatment of ORS due to his experience treating this condition and he has published several peer-reviewed articles on laparoscopic management of ORS.
A listing of over 226 of Dr. Nezhat’s research articles can be found at the PubMed search engine, which pulls references and abstracts from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) database maintained at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).